- Home
- Catalog
- Military Satellites & Space Systems
- KH-11 Reconnaissance Satellite
KH-11 Reconnaissance Satellite


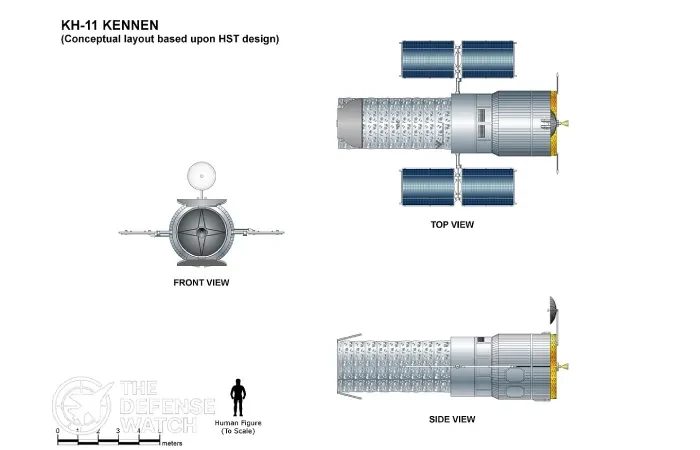
Full Specifications
1. General Information
| System Name | KH-11 Advanced Optical Reconnaissance Satellite |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed Martin |
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Type / Role | Military Reconnaissance / ISR Satellite |
| In Service | Yes |
| Year Introduced | 1976 |
| Unit Cost | USD 600–700 Million Estimated per Satellite |
2. Performance & Capabilities
| Orbit Type | Low Earth Orbit LEO |
| Operational Altitude | 250–500 km |
| Operational Inclination | 97.8° Sun Synchronous |
| Imaging / Sensor Type | Optical / Infrared / ELINT |
| Resolution / Accuracy | Sub meter optical resolution |
| Revisit Time / Coverage | 24–72 hours per location |
| Mission Duration | 7–10 years typical |
3. Payload & Sensor Specifications
| Primary Sensor | Optical Telescope / Multi Spectral Imager |
| Secondary Sensor | Infrared or ELINT Payload |
| Data Transmission | Encrypted SATCOM / X-Band Communication |
| Imaging Capability | Day and Night, Multi Spectral, Panchromatic |
| Payload Weight | 2,500–3,500 kg |
| Onboard Power | Solar Arrays, 3–5 kW |
4. Guidance, Control & Communication
| Attitude Control System | Reaction Wheels plus Hydrazine Thrusters |
| Orbit Control | Chemical and Electric Propulsion |
| Communication Link | X-Band / Ka-Band / Military SATCOM |
| Data Encryption | AES-256 Military Grade |
| Telemetry & Command System | Secure Ground Control Network |
5. Launch & Deployment
| Launch Vehicle | Atlas V / Delta IV / Long March 3B |
| Launch Site | Vandenberg AFB, Cape Canaveral, Taiyuan |
| Deployment Orbit | LEO / GEO / Sun Synchronous |
| Launch Mass | 4,500–5,500 kg |
| Deployment Method | Rocket launched, Direct Injection to Orbit |
6. Operational & Command Use
| Primary Operators | USA NRO / NGA / Air Force |
| Global Coverage | Yes with ground station network |
| Combat Proven | Yes |
| Typical Missions | Reconnaissance, Targeting, ELINT, Early Warning |
| Notable Feature | High Resolution Optical Imaging, Encrypted Comms |
7. Future & Experimental Use
| Planned Upgrades | Improved sensors, AI processing, longer life span |
| Replacement / Next Gen | KH-12 / FIA successors |
| Experimental Variants | Multi Spectral ISR, Counter Space Awareness |
| International Collaboration | Minimal and Classified |
PROS
- Extremely high resolution optical imagery
- Real time encrypted data transmission
- Proven operational history
- Global coverage capability
- Supports multiple intelligence missions
CONS
- Very high development and operating cost
- Classified details limit transparency
- Vulnerable to anti satellite threats
- Limited revisit time compared to large constellations
- Long development and replacement cycles
KH-11 Advanced Reconnaissance Satellite
The KH-11 reconnaissance satellite is one of the most important space based intelligence assets operated by the United States. Developed during the Cold War and continuously upgraded, it forms the backbone of U.S. optical intelligence gathering from orbit.
Manufacturer and Mission Role
The KH-11 program was developed by Lockheed Martin for U.S. intelligence agencies, including the National Reconnaissance Office. Its primary role is intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance, often referred to as ISR. The system supports strategic warning, military planning, arms control monitoring, and real time battlefield awareness.
Core Capabilities and Technology
KH-11 operates in low Earth orbit and uses a large optical telescope with digital imaging sensors. Unlike early film return satellites, KH-11 transmits imagery directly to ground stations using encrypted satellite communications. The satellite can collect detailed images day and night and is believed to integrate infrared and electronic intelligence payloads in later variants.
With sub meter optical resolution, KH-11 can identify military equipment, infrastructure changes, and troop movements. Its sun synchronous orbit allows consistent lighting conditions, improving image comparison over time. Advanced attitude control systems enable precise targeting and rapid retasking.
Operational Use
KH-11 satellites have been used in nearly every major U.S. military operation since the late 1970s. They support combat operations, crisis monitoring, treaty verification, and global security assessments. Data collected is shared across U.S. defense and intelligence organizations to support decision making at the highest levels.
KH-11 Satellite Price
The KH-11 is not commercially sold. Estimated unit cost ranges from USD 600 to 700 million per satellite, reflecting advanced sensors, secure communications, and classified ground infrastructure. Total program costs are significantly higher due to launch, operations, and data processing networks.
FAQs
It is used for military reconnaissance, surveillance, and intelligence collection.
Yes, upgraded versions remain in service.
It is believed to achieve sub meter optical resolution.
U.S. intelligence agencies, primarily the NRO.
It can transmit near real time imagery to ground stations.
Get real time update about this post category directly on your device, subscribe now.
Reviews
Disclaimer Note
The information provided on TheDefenseWatch.com is for general informational purposes only. While we strive to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and timeliness of our content regarding defense and aerospace products, technologies, and specifications, we cannot guarantee that all information is 100% accurate or up-to-date due to the evolving nature of military technology and classified data.TheDefenseWatch.com does not warrant the reliability, suitability, or availability of the information for any specific purpose. Users are advised to consult official sources, such as manufacturers, government publications, or defense agencies, for precise and verified data before making decisions based on our content.We are not affiliated with any defense manufacturers, governments, or military organizations mentioned. Opinions, reviews, and ratings reflect expert analysis but are subjective and should not be considered endorsements. TheDefenseWatch.com is not responsible for any errors, omissions, or consequences arising from the use of this website’s content.External links are provided for convenience and do not imply endorsement. TheDefenseWatch.com reserves the right to update or modify content without prior notice. By using this website, you agree to our Privacy & Cookies Policy.




























