Table of Contents
US Military Satellites Counter Russian Satellite Jamming Threats in 2025
US military satellites face unprecedented challenges from Russian satellite jamming operations as space warfare intensifies in 2025. The United States Space Force and Department of Defense have deployed sophisticated anti-jamming technologies and operational tactics to protect critical space assets from electronic interference, ensuring continuous communication, navigation, and reconnaissance capabilities during heightened geopolitical tensions.
Russian electronic warfare capabilities targeting satellite jamming systems have evolved significantly since 2022, prompting American defense officials to accelerate countermeasure development. These threats include ground-based jammers, co-orbital interference platforms, and cyber-intrusion attempts designed to disrupt GPS signals, military communications, and intelligence-gathering satellites that underpin U.S. military operations worldwide.
Advanced Anti-Jamming Technologies Deployed in 2025
The U.S. Space Force has integrated multiple layers of protection into its satellite constellation architecture. Modern US military satellites now incorporate frequency-hopping spread spectrum technology, which rapidly switches transmission frequencies thousands of times per second, making jamming attempts significantly more difficult to sustain.
Adaptive nulling antennas represent another breakthrough in satellite resilience. These sophisticated systems detect jamming signals and electronically steer reception patterns away from interference sources while maintaining connections with legitimate ground stations. According to Space Force officials, these antennas have reduced successful jamming incidents by approximately 60% compared to legacy systems.
The Military Code (M-Code) GPS signal, fully operational across the constellation in 2025, provides encrypted navigation data resistant to spoofing and jamming. This advanced signal structure delivers positioning accuracy within centimeters even in contested electromagnetic environments, ensuring precision-guided munitions and autonomous systems maintain operational effectiveness.
Russian Jamming Capabilities and Tactical Applications
Russian satellite interference operations have become increasingly sophisticated, utilizing both mobile and fixed ground stations capable of targeting specific orbital paths. The Krasukha-4 and Moskva systems represent Russia’s most advanced jamming platforms, capable of disrupting satellite communications across multiple frequency bands simultaneously.
Intelligence assessments indicate Russian forces have deployed these systems near conflict zones and strategic borders, creating electronic warfare bubbles that complicate NATO and allied operations. These threats extend beyond tactical jamming to include cyber intrusions targeting satellite ground control stations and attempts to physically maneuver satellites into collision courses.
The Space Force maintains continuous monitoring of Russian co-orbital satellites exhibiting suspicious behavior patterns. Several incidents in 2024 involved Russian inspector satellites approaching within dangerous proximity of American assets, raising concerns about potential kinetic attacks or close-range electronic warfare operations.
Space Domain Awareness and Real-Time Threat Detection
Enhanced space situational awareness capabilities allow the United States to detect and characterize jamming attempts within seconds. The Space Surveillance Network, comprising ground-based radars, optical telescopes, and space-based sensors, tracks over 30,000 objects in orbit and monitors the electromagnetic spectrum for interference signatures.
Machine learning algorithms analyze telemetry data from satellite constellations, identifying anomalies that indicate jamming or spoofing attempts. These artificial intelligence systems have reduced false alarm rates by 75% while accelerating response times to genuine threats, enabling operators to implement countermeasures before mission-critical disruptions occur.
The National Space Defense Center coordinates responses to detected threats, integrating data from military, intelligence, and commercial partners. This collaborative approach ensures comprehensive threat assessment and enables synchronized countermeasures across multiple orbital regimes and operational domains.
Resilient Satellite Architecture and Operational Redundancy
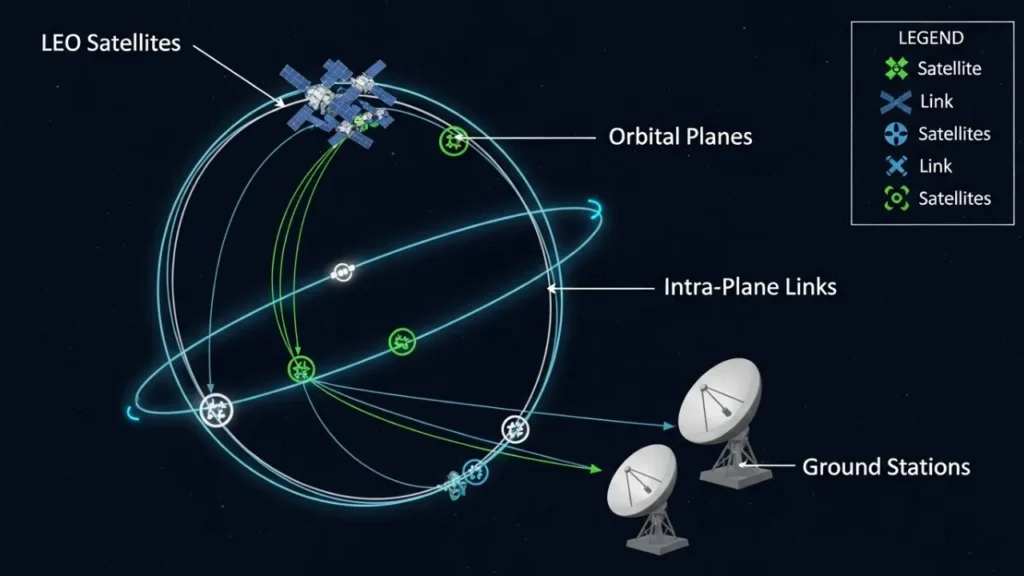
The Pentagon’s shift toward proliferated low Earth orbit (LEO) constellations enhances resilience against Russian satellite jamming campaigns. Rather than relying on a small number of expensive satellites in geosynchronous orbit, the military now deploys hundreds of smaller, more affordable satellites that distribute mission capabilities across multiple platforms.
This architectural transformation, exemplified by the Space Development Agency’s Proliferated Warfighter Space Architecture, ensures that jamming one or several satellites does not compromise overall mission effectiveness. The constellation design incorporates mesh networking capabilities, allowing satellites to route communications through alternative pathways when primary links are disrupted.

Cross-linking between satellites enables on-orbit data processing and transmission that bypasses potentially compromised ground stations. This capability proved critical during recent exercises simulating large-scale electronic warfare scenarios, where military communications maintained 95% availability despite persistent jamming attempts.
International Cooperation and Allied Space Defense
NATO allies have intensified cooperation on space defense capabilities, sharing threat intelligence and coordinating responses to jamming incidents. The Combined Space Operations Center at Vandenberg Space Force Base integrates allied personnel who provide real-time input on electromagnetic interference affecting coalition operations.
European partners contribute advanced sensor networks and complementary satellite capabilities that enhance collective resilience. France’s Syracuse military communications satellites and Germany’s SARah reconnaissance system provide alternative channels when American assets face interference, demonstrating the strategic value of multinational space cooperation.
Commercial satellite operators increasingly support military communications through services like the Space Force’s Commercial Satellite Communications Office. These partnerships provide additional bandwidth and routing options that complicate adversary targeting efforts, as distinguishing military from commercial traffic becomes more challenging.
Future Developments and Emerging Technologies
Quantum encryption technology represents the next frontier in securing satellite communications against interference and interception. The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) continues developing quantum key distribution systems for space applications, promising theoretically unbreakable encryption that renders jamming and cyber intrusions ineffective.
Directed energy systems for active defense may provide future satellites with offensive counter-jamming capabilities. Laser communications systems not only offer jam-resistant data transmission but could potentially disable adversary jamming equipment through precision targeting, though such capabilities remain in experimental phases.
The Space Force’s investment in autonomous orbital maneuvering enables satellites to physically avoid co-orbital threats while maintaining mission coverage. Advanced propulsion systems allow frequent orbital adjustments without depleting fuel reserves, ensuring long-term survivability in contested space environments.
Strategic Implications and Deterrence Considerations
The ongoing space warfare competition between the United States and Russia reflects broader geopolitical tensions and the increasing militarization of orbital domains. While both nations maintain official positions supporting peaceful space exploration, operational realities demonstrate that space has become a critical warfighting domain requiring robust defensive capabilities.
American officials emphasize that anti-jamming technologies and resilient satellite architectures serve deterrent purposes, convincing potential adversaries that space-based attacks cannot achieve decisive advantages. This deterrence-by-denial strategy aims to prevent escalation while protecting the space assets that underpin terrestrial military operations.
The development of space norms and rules of engagement remains incomplete, creating strategic ambiguity about acceptable behavior in orbit. The United States advocates for transparency measures and behavioral norms that reduce the risk of miscalculation, though enforcement mechanisms remain largely absent in the international space governance framework.
Analysis: The Evolving Space Security Landscape
The proliferation of anti-satellite capabilities among major powers has transformed space from a sanctuary to a contested operational domain. US military satellites must now operate under the assumption of persistent threats, requiring redundancy, resilience, and rapid response capabilities that previous generations of space systems never needed. This shift represents both a significant investment challenge and a strategic imperative, as military effectiveness increasingly depends on assured space access.
The technological competition between American defensive systems and Russian jamming capabilities will likely continue escalating, driving innovation on both sides. However, the fundamental advantage remains with defensive systems, as the physics of satellite communications and the vast distances involved favor defenders who can implement frequency diversity, encryption, and redundant pathways. The key question for 2025 and beyond is whether this technological edge translates into effective deterrence or merely postpones more dangerous forms of space conflict.
FAQs
Russian satellite jamming can disrupt GPS navigation, military communications, and intelligence gathering. However, modern US military satellites employ anti-jamming technologies like frequency hopping and encrypted signals that maintain 95%+ availability even during interference attempts.
Key technologies include frequency-hopping spread spectrum systems, adaptive nulling antennas, Military Code GPS signals, quantum encryption (in development), and proliferated LEO satellite constellations that provide redundancy and resilience against electronic warfare attacks.
No. Jamming creates temporary disruptions but cannot permanently disable satellites. US Space Force maintains multiple backup systems, alternative communication pathways, and rapid countermeasures that restore functionality within seconds to minutes of detected interference.
The Space Surveillance Network uses ground-based radars, optical telescopes, and space-based sensors combined with AI-powered algorithms to monitor the electromagnetic spectrum. These systems detect jamming signatures within seconds and automatically alert operators to implement countermeasures.
Anti-jamming capabilities ensure military forces maintain command and control, precision navigation, and intelligence gathering during conflicts. These technologies provide deterrence by demonstrating that space-based attacks cannot achieve decisive advantages, potentially preventing escalation in space warfare.
Get real time update about this post category directly on your device, subscribe now.

3 comments
[…] Jamming military communications and satellite navigation signals […]
[…] military operations in challenged electromagnetic environments. According to Lockheed Martin, the GPS III satellite family provides three times better accuracy, eight times improved anti-jamming capabilities, and […]
[…] funds 11 National Security Space Launch missions, maintaining the cadence necessary to deploy military satellites and ensure access to space remains available for national security purposes. These launches support everything from […]